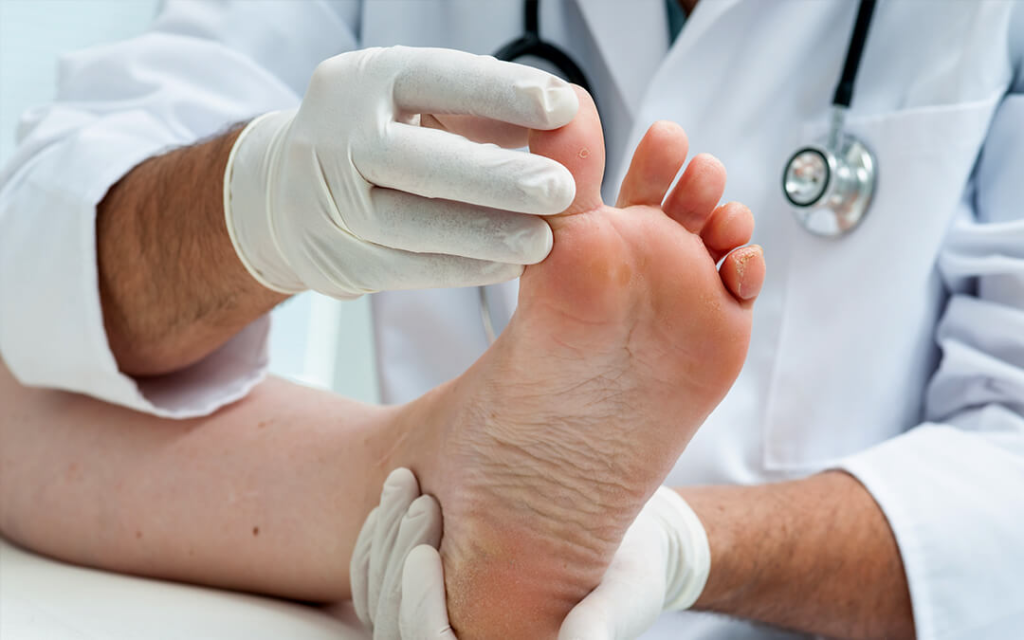
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it has consequences that go far beyond just managing blood sugar levels. One aspect of diabetes that often doesn’t receive enough attention is its profound impact on foot health. Diabetes doesn’t just mess with glucose regulation; it also disrupts the circulatory and nervous systems in your feet, setting the stage for potentially serious foot problems. In this article, we’ll dive into the significant effects of diabetes on foot health and explore effective strategies for prevention and management. By understanding these crucial aspects, both healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes can work together to mitigate the adverse outcomes associated with this condition.
Understanding the Connection: How Diabetes Impacts Foot Health
Diabetes isn’t limited to controlling blood sugar; it wields a powerful influence on your feet. Many people underestimate how diabetes can wreak havoc on their foot health, often overlooking the potential complications. Diabetes throws a wrench into glucose regulation and disrupts circulation and nerve functions in your feet, creating an environment ripe for severe foot issues. This article aims to shed light on how diabetes affects foot health and provides valuable insights into prevention and management techniques. By grasping these essential aspects, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of foot complications associated with this complex disease.
The Unseen Foot Complications in Diabetes: Prevention and Early Detection
Diabetes silently brews foot complications that often remain unnoticed until they reach critical levels. As diabetes disrupts your body’s ability to regulate glucose levels, it also wreaks havoc on the circulatory and nervous systems in your feet. This can result in reduced blood flow and nerve damage, significantly increasing the risk of infections and ulcers. Early detection is paramount to preventing these complications from escalating to the point of foot amputations.
Prevention is the key to maintaining good foot health for individuals with diabetes. Regular self-examinations of your feet can help identify any changes or abnormalities early on. Keeping your blood sugar levels in check through medication, diet, and exercise is crucial for reducing the risk of foot complications. Equally important is wearing well-fitting shoes that provide proper protection and support for your feet.
Taking Proactive Measures: Strategies for Keeping Your Feet Healthy
Diabetes exerts a profound influence on foot health, but you can take steps to protect your feet. This article explores preventive measures such as self-examination, proper foot hygiene, and wearing comfortable footwear. It also offers insights into managing existing foot problems through regular podiatric check-ups and treatment techniques. By incorporating these strategies into your daily life, you can significantly improve your overall foot health and quality of life.
Complications From Lack of Sleep
If you get less than 7 hours of sleep per night regularly, your diabetes will be harder to manage. Too little sleep can:
- Increase insulin resistance.
- Make you hungrier the next day and reduces how full you feel after eating.
- Make you more likely to reach for junk foods—those that are high in carbs and sugar.
- Make it harder to lose weight.
- Raise blood pressure and seriously increase the risk of a heart attack.
- Make your immune system less able to fight infections.
- Increase your risk of depression and anxiety.
Tips to Get More Zzz’s
Sleep quality is as important as how many hours you get. Signs you aren’t getting good sleep may include:
- Not feeling rested even after sleeping enough hours.
- Repeatedly waking up during the night.
- Having symptoms of sleep disorders (such as snoring or gasping for air).
It’s common to stay up late and get up early during the week, then sleep in on the weekend. You may hope to catch up on the hours you missed, but your brain can’t use these added hours.
One of the best things you can do is to wake up and go to bed at around the same time every day, even on weekends, making sure you get enough quality sleep consistently. These tips can help:
- Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, relaxing, and cool. Experts recommend a temperature of 65 degrees for your best rest.
- Remove electronic devices such as TVs, computers, and smartphones from the bedroom.
- Get some physical activity during the day.
- Mentally unwind and relax before bedtime.
- Have a routine that gets you ready for bed, like taking a shower, reading, or writing in a journal.
- Get in bed only when you’re tired.
Here are a few things to avoid:
- Afternoon and evening caffeine. It can affect your body for up to 8 hours.
- Alcohol in the evening. It can affect how you breathe when you sleep. It can also wake you up and affect your sleep quality.
- Large meals late at night. Eating late can cause indigestion and higher blood sugar levels overnight.
- Naps after 3 p.m. This can make you less tired when it’s time for bed.
- Nicotine. It acts like caffeine.
If you still have problems getting a good night’s rest, talk with your doctor or contact the Alaska Sleep Clinic.
Managing Foot Complications: Treatment and Care for Diabetic Patients
Effectively managing foot complications is a critical aspect of care for diabetic patients. Diabetes can take a toll on foot health by compromising circulation and nerve function. It disrupts your body’s ability to regulate glucose levels, leading to severe complications like foot ulcers and neuropathy. Preventive measures, such as maintaining proper foot hygiene, regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, and wearing appropriate footwear, are essential components of managing these complications.
Treatment for diabetic foot complications requires a comprehensive approach that includes wound care, infection control, and glycemic control. Techniques like wound debridement and off-loading are commonly used to promote healing and prevent further deterioration. In cases of infected wounds, antibiotics may be necessary. Additionally, keeping your blood glucose levels within target ranges through medication and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for optimal management.
In summary, diabetes poses significant challenges for foot health due to its adverse effects on circulation and nerves. However, with proactive prevention measures and a comprehensive treatment plan, you can effectively manage foot complications associated with diabetes. This includes promoting wound healing, preventing infections, and maintaining glycemic control. By taking these steps, you can protect your feet and overall well-being, ensuring that diabetes doesn’t compromise your quality of life.










