Sleep Deprivation in Adults
In 2014, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classified sleep deprivation as an epidemic in the United States with more than 70 million adults currently suffering from the condition. That’s one third of the U.S. adult population.
Groups with the highest percentage of sleep deprivation are Native Hawaiians/Pacific Islanders at 46.3% and Blacks at 45.8% then Asians at 37.5%, Hispanics at 34.5%, and Whites at 33.4%. – CDC
Sleep deprivation can affect all aspects of our lives, and some effects are much more serious than simply nodding off at work or being irritable. For one, there is evidence that losing sleep regularly is associated with chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
According to the CDC, heart attack, coronary heart disease, stroke, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cancer, arthritis, depression, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes occurrences were higher in U.S. adults who suffer from sleep deprivation or what CDC calls “Short Sleep Duration,” which is less than 7 hours of sleep per night.
Recently, John Hopkins published an infographic with four categories of effects of sleep deprivation. They are: weight, health, brain effects, and safety. For instance, did you know the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes is three times as high for those who are chronically sleep deprived?
Health & Weight
Some study findings show that lack of sleep doubled the risk of death from all causes including cardiovascular disease.
You are also more at risk for obesity due to the hormonal imbalance introduced by sleep deprivation. You crave sweet, salty, and starchy foods because you have higher levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin and lower levels of leptin, the appetite-control hormone. Sleep deprivation can also affect your brain. You have a 33% higher risk for dementia if you suffer from lack of sleep.
Safety
Sleeplessness is also connected to other severe consequences. It is estimated that drowsy driving causes 1,550 deaths and 40,000 injuries annually in the United States.
There is even evidence that sleep deprivation may make you less empathetic.

The Little One is Tired
According to the Children’s Sleep Apnea Association, an estimated 1 to 4% of children suffer from sleep apnea, including kids between the ages of 2 and 8 years old. It is a common belief that children will eventually grow out of pediatric sleep disorders, but new evidence suggests that may not be the case. Studies have shown sleep apnea is linked to childhood obesity, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and cognitive functioning ability.
Some mommy bloggers made suggestions on how to establish and keep an ongoing bedtime routine with your youngsters. Most bloggers agree you should stick with a nightly schedule and sleep hygiene routine that includes taking a bath, brushing teeth, cleaning the bedroom, and dimming the lights.
We start our routine at 7:30 pm. I don’t like to rush them, so I try to get them to relax and wind down at least an hour before the desired bedtime…my kids take a bath or shower, have a snack (no chocolate or sweets!), brush their teeth, read, and then it’s time for me or Dad to tuck them in.
– Jeannette Kaplun, Mommy Blogger at Hispana Global and mother of two.
Sleepless in School
The recommended amount of sleep for high school and college students is 8-10 hours per night, with anything from 8½ (short sleep duration) to 11 hours considered appropriate. According to the CDC, nearly 69% of high school students sleep less than 8 hours a night, with an astounding 76.6% of seniors not getting enough sleep.
Additionally, up to 60% of college students do not get enough sleep on a regular basis.
Another study found that sleep-deprived students were more likely to engage in unhealthy behavior such as drinking, fast driving, and getting into physical fights. Sleep deprivation is also a good predictor of poor academic and athletic performance and drowsy driving.
College students who experienced even one additional night of poor sleep per week were more likely to drop a course (10%) and see a drop in their cumulative GPA (by 0.02). Sleep deprivation ranked the same if not higher than other factors that negatively affect academic success including binge drinking and drug use.
To get better sleep, it is recommended that high school and college students make the following changes:
Set and stick to a bedtime routine and sleep schedule
Practice sleep hygiene
Create a peaceful sleep environment
Eliminate caffeine three hours before bedtime
Avoid using mobile devices, computer, or tv 1-2 hours before going to sleep
Don’t go to bed hungry, instead eat a small snack
Avoid working out right before bedtime
Meditate or practice light yoga to relax
Other age groups affected by sleep loss include the elderly and people with certain diseases including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia. Aging can affect our sleep patterns due to a number of factors including hormonal changes associated with aging and the increased likelihood of taking more medications and experiencing side effects. It is recommended that you work with your primary care physician to determine the best course of treatment.
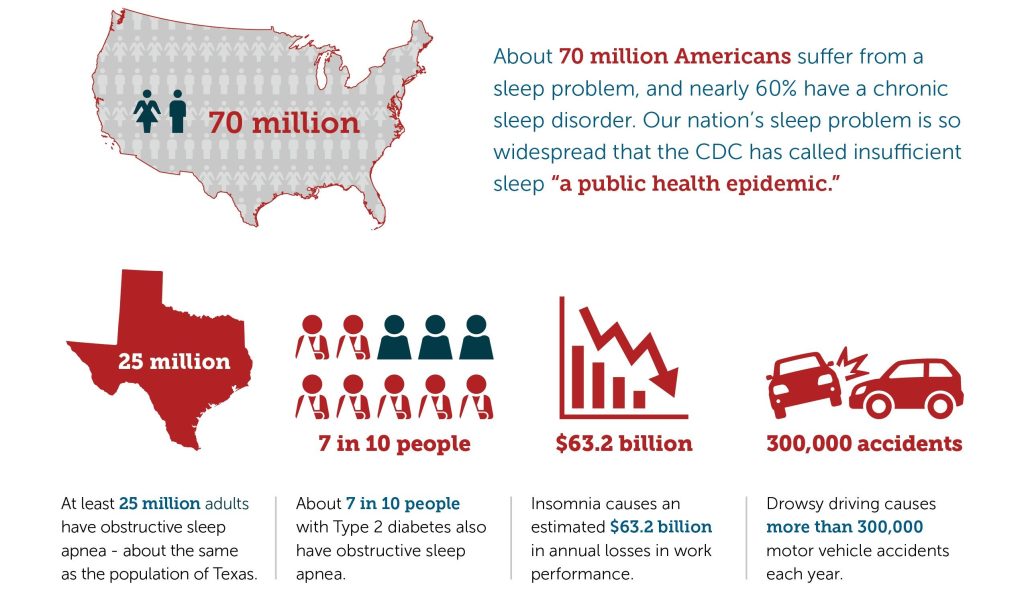
The average U.S. worker loses 11 days of productivity per year due to insomnia. That’s $2,280 per year. The total loss is a whopping $63.2 billion per year. What this could mean for you is missing out on a promotion or a superior performance review.
Unfortunately, our corporate culture only contributes to this by promoting the idea that sleep is not a required commodity. In other words, we think sleep is a luxury saved for vacations and weekends, not something we need for proper health.
A few companies have begun to pay attention to the field of sleep medicine and recent research that has shown the negative effects of poor sleep on employee health, work productivity, and ballooning insurance costs. A recently Fatigue Cost Calculator developed by Brigham and Women’s Hospital for the National Safety Council can provide estimates of the cost of poor sleep health for an employer. Google, Goldman Sachs, and Johnson & Johnson, to name a few, are some of these companies.
At Google, for instance, sleep experts have been invited to the company’s locations to share information with employees regarding sleep deprivation, jet lag, and the restorative power of deep sleep.
Light is the enemy of sleep. – Dr. Budhiraja
More From The Best
Budhiraja says that sleep works to regenerate our bodies including our brains and our muscles. The brain progresses through different stages of sleep every 90 minutes or so: light sleep, deep sleep, and REM stage, which is the dream phase of sleep.
“During sleep, muscle tone goes down,” says Budhiraja. “Relaxation of muscle is even greater during the dream stage of sleep.” He explains that many areas of the brain also relax during the sleep and the rate of brain metabolism decreases, except in REM phase, where the brain activity and energy use may be even higher than when awake. REM and non-REM sleep may be responsible for different aspects of memory consolidation.
A Little TLC
Based on his research, Budhiraja recommends you make three lifestyle changes scientifically proven to improve your sleep. He calls it TLC or temperature, light, and calming your mind to get better sleep.
The cooler your body, the better sleep you can get. -Dr. Budhiraja
First, there is temperature. When you go to sleep, you do not want your room too warm or too cold. The ideal room temperature to promote better sleep is between 65 and 70 degrees.
Light is another factor proven to affect sleep. If there is too much light in your bedroom, especially artificial light, it can stop the production of melatonin in your brain, the hormone related to sleep. “Light is the enemy of sleep,” says Budhiraja. Cellphones and other mobile devices are blue light sources and major disruptors of sleep. “Smartphones are shown to decrease sleep by up to half an hour.” Budhiraja suggests putting your phone down one to two hours before you go to bed.
Calming your mind completes the treatment trio and is also something we can control, although it may be difficult for some to do. Meditating or deep breathing before going to sleep has been found to decrease anxiety and depression. In fact, studies report meditation is associated with decreased activity in the default mode network or DMN, which is a part of the brain related to mind wandering and thinking about the self.

Medication and Treatments
Holistic
Some popular holistic supplements include melatonin, valerian root, and herbal teas such as chamomile tea. According to Budhiraja, melatonin is likely the most studied sleep supplement. As a sleep hormone produced naturally in the body, it tells the brain when it’s time to fall asleep. The dosage is up for debate—over the counter pills are usually available in 1mg or 3mg or higher doses—starting at a lower dose and increasing the dose if needed is a good idea. Melatonin is considered to be a fairly well-tolerated sleep treatment; however, it is not a cure-all for sleep disorders and may only be effective for certain individuals. It is more likely to be effective in individuals who have delayed sleep phase syndrome- a condition in which people fall asleep late and wake up late. It can be also effective in preventing or treating jet lag.
Other alternative solutions include making the bedroom as dark as possible and/ or the addition of a white noise machine to your sleep routine. It is estimated that nearly 75% of Americans said that a quiet room is important to getting good sleep. Lastly, there is taking your grandmother’s age-old advice: drink a warm cup of milk before going to bed.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is a very effective therapy where a psychologist or another trained professional can help you identify and address your thoughts and behaviors that may be contributing to poor sleep. It even can be delivered through online programs.
Over-The-Counter
Over-the-counter medications include diphenhydramine (Benadryl, Aleve PM, etc.) or doxylamine succinate (Unisom). These sleep aids have side effects including drowsiness and leaving you feeling groggy the next day. Furthermore, the body can quickly develop tolerance to some of these medications.
Prescription Medication
Finally, there are prescription medications. According to Budhiraja, medications should generally be your last resort in seeking help to get better sleep, and if used, should usually be used over short-term. They can cause several side effects- drowsiness, dizziness, diarrhea, grogginess or feeling as if drugged. In addition, after taking some of these medicines, people may get up out of bed while not being fully awake and do an activity that they do not know they are doing- including driving. The next morning, they may not remember that they did anything during the night. “The body can also develop tolerance to these medications, requiring progressively increasing doses or more potent medicines,” he says.
Before Turning Off the Lights
Most of us have faced a sleepless night or two in our lifetimes. We’ve laid awake and listened to a leaky faucet go drip, drip, drip into the wee hours of the night. Worse, we are one of the 70 million people in the United States who suffer from a lack of sleep or who have a sleep disorder.
We’re tired new parents, or college students cramming for an exam, or a software engineer who works 60 hours or more a week, or are getting older and are finding it harder to sleep.
Seventy million: that’s more than a third of the population across the nation.
Scientific studies have proven the health ramifications of sleep deprivation and what it does to our bodies, minds, and everyday lives. It is an epidemic that not only affects us as adults but is also affecting our nation’s kids.
We can take countermeasures to gt more and better sleep, steps that have been proven to work by scientific studies. We can give ourselves some TLC to promote better sleep, which can, in turn, restore us to our full capacity. Because really, don’t we just want our best sleep every night, especially in this age of high stress? We want that great sleep where we wake up refreshed and ready to take on the day.
Call Alaska Sleep Clinic today for your free sleep assessment.












